Introduction
Overview
Teaching: 5 min
Exercises: 5 minQuestions
How to get to your cluster?
How to get ready to submit the workflow?
Objectives
Get your GCP environment ready to run an argo workflow
Scale your cluster up to 4 nodes
Get the tools running to observe the working processes
Access your GKE Cluster
For the CMS Open data Workshop 2023, we have added you to a GCP project where we will provide temporary resources to run an Argo Workflow. Before we get into details please follow the following steps to get things started!
Find your cluster
- Go to the Google Kubernetes Engine page
- You should see a listing of clusters.
- Find the number of your cluster in the email you have received and select your cluster in the list.
Connect to the cluster
- Now go back to the cluster listing page, click on the three vertical dots, and choose “connect”.
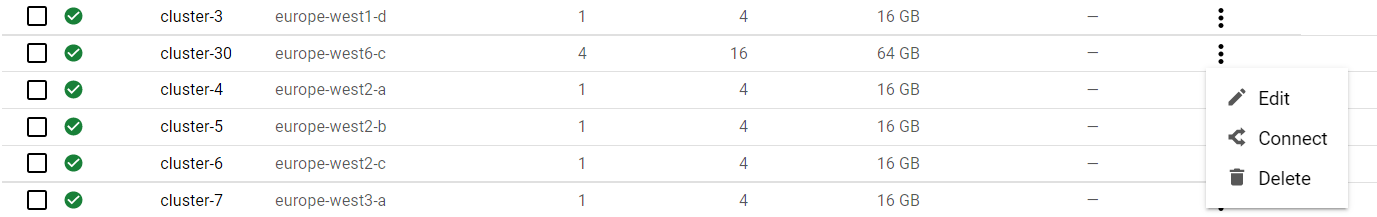
- Click on “RUN IN CLOUD SHELL” to connect to your cluster.

- In the cloud shell press Enter after the command and authorize cloud shell in the pop-up window that opens
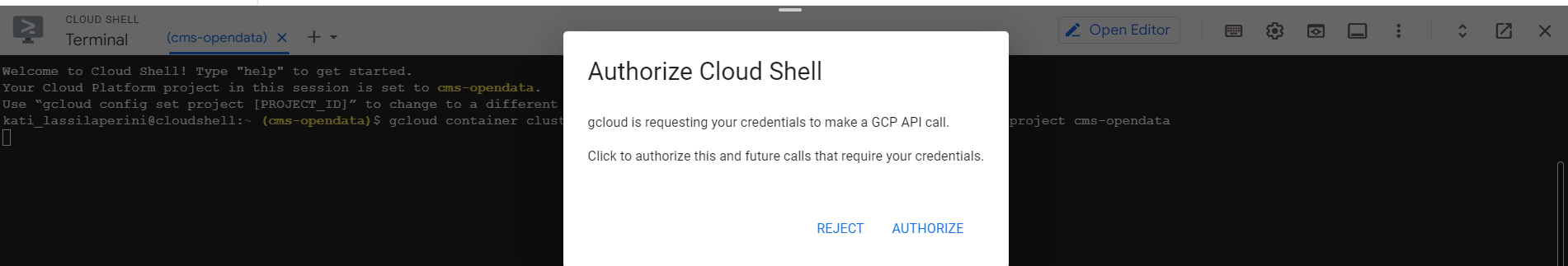
- If requested, submit the command
gcloud auth loginand follow the link the get the authorization code.
A persistent disk has already been created for you, as well as persistent volumes and persistent volume claims. Some other resources are already available, and you will see them with
$ kubectl get all -n argo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/http-fileserver-1-5b85db44df-84ppt 1/1 Running 0 30m
pod/nfs-server-1-69db86f88-kvbkb 1/1 Running 0 32m
pod/pv-pod 1/1 Running 0 30m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/http-fileserver-1 LoadBalancer 10.127.203.234 35.195.41.247 80:32703/TCP 32m
service/nfs-server-1 ClusterIP 10.127.194.124 <none> 2049/TCP,20048/TCP,111/TCP 32m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/http-fileserver-1 1/1 1 1 30m
deployment.apps/nfs-server-1 1/1 1 1 32m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/http-fileserver-1-5b85db44df 1 1 1 30m
replicaset.apps/nfs-server-1-69db86f88 1 1 1 32m
Argo
Argo resources
Deploy the argo resources needed to run the example workflow with
kubectl apply -n argo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-workflows/master/manifests/quick-start-postgres.yaml
If Ctrl-v does not work for pasting the command, try Shift-Ctr-v.
Argo command-line interface
To submit the workflow from the cloud shell, you will need the argo command-line interface. You can download the binary and move it to its respective path with the following commands:
# Download the binary
curl -sLO https://github.com/argoproj/argo-workflows/releases/download/v3.4.7/argo-linux-amd64.gz
# Unzip
gunzip argo-linux-amd64.gz
# Make binary executable
chmod +x argo-linux-amd64
# Move binary to path
sudo cp ./argo-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/argo
# Test installation
argo version
If your cloud shell gets disconnected and argo is not available in the new cloud shell, you can repeat the sudo cp ... command to have it in place again.
Submit the workflow
Now fast forward: to make sure that the workflow makes it in time to finish during the hands-on session, submit it right now. We will explain the details while the workflow is running.
Get the workflow file with
curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cms-opendata-analyses/PhysObjectExtractorTool/odws2023/PhysObjectExtractor/cloud/argo_poet.yaml
The workflow defines the persistent volume in which the output is stored. Edit the workflow to replace <NUMBER> to correspond to your cluster number. You can use an editor available in cloud shell for editing, or use command line editors such as vim or nano if you are familiar with them. Or if you like, use the following command to replace the string, but replace YOUR_CLUSTER_NUMBER in it with the number of your cluster
sed -i 's/<NUMBER>/YOUR_CLUSTER_NUMBER/' argo_poet.yaml
Then submit the workflow with
argo submit argo_poet.yaml -n argo
Check that it got running with
argo get @latest -n argo
Get your services
To get the external IP of both the Argo GUI (with which you can follow the workflow) and the http server (through which you can download the outputs), run the following command:
kubectl get svc -n argo
Http File Server
In a new tab open <EXTERNAL-IP>, no need to add anything, just paste the external IP of your http-fileserver-<NUMBER> from the output of the command above.
You can also use the following command to print out the exact URL (replace <NUMBER> with the number of your cluster)
echo "http://$(kubectl get services -n argo http-fileserver-<NUMBER> -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')"
Argo GUI
To get the Argo GUI running, run the following command:
kubectl -n argo port-forward deployment/argo-server 2746:2746
Once it has started forwarding the port, we will have to manually enable the port. Open a new cloud shell tab and run the following command:
lynx --accept_all_cookies --source https://localhost:2746 >/dev/null 2>&1
Finally, patch the service with:
kubectl patch svc argo-server -n argo -p '{"spec": {"type": "LoadBalancer"}}'
Since it is creating an external ip, wait a couple minutes. You can check if it is ready with:
kubectl get svc -n argo
To access the Argo GUI, open a new browser tab with the following IP address: https://<EXTERNAL-IP>:2746, replacing <EXTERNAL-IP> with the corresponding external IP of your argo-server-<NUMBER> from the output of the command above.
You can also use the following command to print out the exact URL
echo "https://$(kubectl get services -n argo argo-server -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}'):2746"
You should now be able to see your workflow in the Argo GUI.
Next
OK, we got it running! Now let’s go to see the details…
Key Points
You can submit the workflow from the Google cloud shell connected to your cluster.