CMS Jets and MET
Overview
Teaching: 10 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
How are jets and missing transverse energy treated in CMS OpenData?
Objectives
Identify jet and MET code collections in AOD files
Understand typical features of jet/MET objects
Practice accessing jet quantities
After tracks and energy deposits in the CMS tracking detectors (inner, muon) and calorimeters (electromagnetic, hadronic) are reconstructed as particle flow candidates, an event can be interpreted in various ways. Two common elements of event interpretation are clustering jets and calculating missing transverse momentum.
Jets
Jets are spatially-grouped collections of long-lived particles that are produced when a quark or gluon hadronizes. The kinetmatic properties of jets resemble that of the initial partons that produced them. In the CMS language, jets are made up of many particles, with the following predictable energy composition:
- ~65% charged hadrons
- ~25% photons (from neutral pions)
- ~10% neutral hadrons
Jets are very messy! Hadronization and the subsequent decays of unstable hadrons can produce 100s of particles near each other in the CMS detector. Hence these particles are rarely analyzed individually. How can we determine which particle candidates should be included in each jet?
Clustering
Jets can be clustered using a variety of different inputs from the CMS detector. “CaloJets” use only calorimeter energy deposits. “GenJets” use generated particles from a simulation. But by far the most common are “PFJets”, from particle flow candidates.
The result of the CMS Particle Flow algorithm is a list of particle candidates that account for all inner-tracker and muon tracks and all above-threshold energy deposits in the calorimeters. These particles are formed into jets using a “clustering algorithm”. The most common algorithm used by CMS is the “anti-kt” algorithm, which is abbreviated “AK”. It iterates over particle pairs and finds the two (i and j) that are the closest in some distance measure and determines whether to combine them:

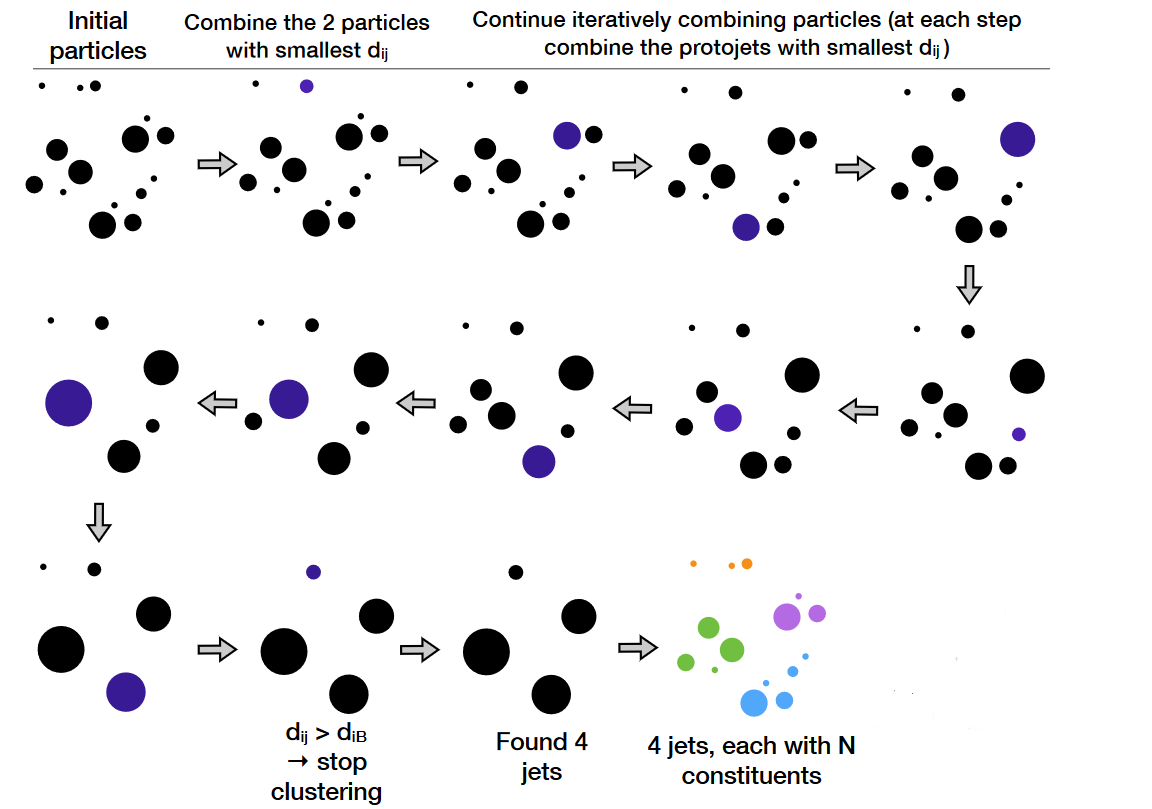
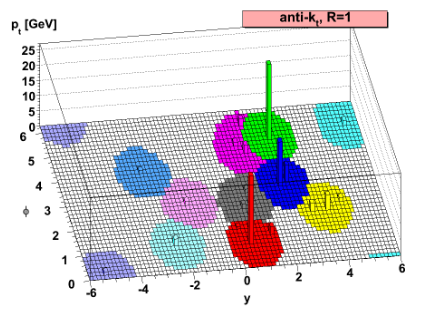
The momentum power (-2) used by the anti-kt algorithm means that higher-momentum particles are clustered first. This leads to jets with a round shape that tend to be centered on the hardest particle. In CMS software this clustering is implemented using the FastJet package.

Pileup
Inevitably, the list of particle flow candidates contains particles that did not originate from the primary interaction point. CMS experiences multiple simultaneous collisions, called “pileup”, during each “bunch crossing” of the LHC, so particles from multiple collisions coexist in the detector. There are various methods to remove their contributions from jets:
- Charged hadron subtraction CHS: all charged hadron candidates are associated with a track. If the track is not associated with the primary vertex, that charged hadron can be removed from the list. CHS is limited to the region of the detector covered by the inner tracker. The pileup contribution to neutral hadrons has to be removed mathematically – more in episode 3!
- PileUp Per Particle Identification (PUPPI, available in Run 2): CHS is applied, and then all remaining particles are weighted based on their likelihood of arising from pileup. This method is more stable and performant in high pileup scenarios such as the upcoming HL-LHC era.
Accessing jets in CMS software
Jets software classes have the same basic 4-vector methods as the objects discussed in the previous lesson. There are two principle ways to interact with jets in the OpenData files: via the reco::Jet class or the pat::Jet class. PAT stands for “Physics Analysis Toolkit”, which is a framework for applying and accessing many common analysis-level algorithms that are used in CMS. The POET features JetAnalyzer.cc to demonstrate working with RECO jets and PatJetAnalyzer.cc to demonstrate working with PAT jets.
In JetAnalyzer.cc
Handle<reco::PFJetCollection> myjets;
iEvent.getByLabel(jetInput, myjets); // jetInput is "ak5PFJets"
for (reco::PFJetCollection::const_iterator itjet=myjets->begin(); itjet!=myjets->end(); ++itjet){
...
jet_e.push_back(itjet->energy());
jet_pt.push_back(itjet->pt());
jet_px.push_back(itjet->px());
jet_py.push_back(itjet->py());
jet_pz.push_back(itjet->pz());
jet_eta.push_back(itjet->eta());
jet_phi.push_back(itjet->phi());
jet_ch.push_back(itjet->charge());
jet_mass.push_back(itjet->mass());
}
In PatJetAnalyzer.cc the jet collection has a different type (and name), and all the energy-related quantities have corrections applied, which will be discussed more in an upcoming lesson.
Handle<std::vector<pat::Jet>> myjets;
iEvent.getByLabel(jetInput, myjets); // jetInput is "selectedPatJetsAK5PFCorr"
for (std::vector<pat::Jet>::const_iterator itjet=myjets->begin(); itjet!=myjets->end(); ++itjet){
...
corr_jet_mass.push_back(itjet->mass());
corr_jet_e.push_back(itjet->energy());
corr_jet_px.push_back(itjet->px());
corr_jet_py.push_back(itjet->py());
corr_jet_pz.push_back(itjet->pz());
}
Particle-flow jets are not immune to noise in the detector, and jets used in analyses should be filtered to remove noise jets. CMS has defined a Jet ID with criteria for good jets:
The PFlow jets are required to have charged hadron fraction CHF > 0.0 if within tracking fiducial region of |eta| < 2.4, neutral hadron fraction NHF < 1.0, charged electromagnetic (electron) fraction CEF < 1.0, and neutral electromagnetic (photon) fraction NEF < 1.0. These requirements remove fake jets arising from spurious energy depositions in a single sub-detector.
These criteria demonstrate how particle-flow jets combine information across subdetectors. Jets will typically have energy from electrons and photons, but those fractions of the total energy should be less than one. Similarly, jets should have some energy from charged hadrons if they overlap the inner tracker, and all the energy should not come from neutral hadrons. A mixture of energy sources is expected for genuine jets. All of these energy fractions (and more) can be accessed from the jet objects.
MET
Missing transverse momentum is the negative vector sum of the transverse momenta of all particle flow candidates in an event. The magnitude of the missing transverse momentum vector is called missing transverse energy and referred to with the acronym “MET”. Since energy corrections are made to the particle flow jets, those corrections are propagated to MET by adding back the momentum vectors of the original jets and then subtracting the momentum vectors of the corrected jets. This correction is called “Type 1” and is standard for all CMS analyses.
In MetAnalyzer.cc we open the particle flow MET module and extract the magnitude and angle of the MET, the sum of all energy
in the detector, and variables related to the “significance” of the MET. Note that MET quantities have a single value for the
entire event, unlike the objects studied previously.
Handle<reco::PFMETCollection> mymets;
iEvent.getByLabel(metInput, mymets); // metInput opens "pfMet"
if(mymets.isValid()){
met_e = mymets->begin()->sumEt();
met_pt = mymets->begin()->pt();
met_px = mymets->begin()->px();
met_py = mymets->begin()->py();
met_phi = mymets->begin()->phi();
met_significance = mymets->begin()->significance();
}
If the PAT process has been run, Type 1 corrected MET is also available in MetAnalyzer.cc:
Handle<reco::PFMETCollection> patmets;
iEvent.getByLabel(metInputPat, patmets); // metInputPat opens "pfType1CorrectedMet"
if(patmets.isValid()){
met_e = patmets->begin()->sumEt();
met_pt = patmets->begin()->pt();
met_px = patmets->begin()->px();
met_py = patmets->begin()->py();
met_phi = patmets->begin()->phi();
}
MET significance can be a useful tool: it describes the likelihood that the MET arose from noise or mismeasurement in the detector as opposed to a neutrino or similar non-interacting particle. The four-vectors of the other physics objects along with their uncertainties are required to compute the significance of the MET signature. MET that is directed nearly (anti)colinnear with a physics object is likely to arise from mismeasurement and should not have a large significance.
Key Points
Jets are spatially-grouped collections of particles that traversed the CMS detector
Particles from additional proton-proton collisions (pileup) must be removed from jets
Missing transverse energy is the negative vector sum of particle candidates
Many of the class methods discussed for other objects can be used for jets