What data and Monte Carlo are available?
Overview
Teaching: 5 min
Exercises: 10 minQuestions
What data and run periods are available?
What data do the collision datasets contain?
What Monte Carlo samples are available?
Objectives
To be able to navigate the CERN Open Data Portal’s search tools
To be able to find what collision data and Monte Carlo datasets there are using these search tools
Data and run periods
We make a distinction between data which come from the real-life CMS detector and simulated Monte Carlo data. In general, when we say data, we mean the real, CMS-detector-created data.
The main data available are from what is known as Run 1 and spans 2010-2012. The first batch of Run 2 data from 2015 was released in 2021. These run periods can also be broken into A, B, C, and so-on, sub-periods and you may see that in some of the dataset names.
Make a selection!
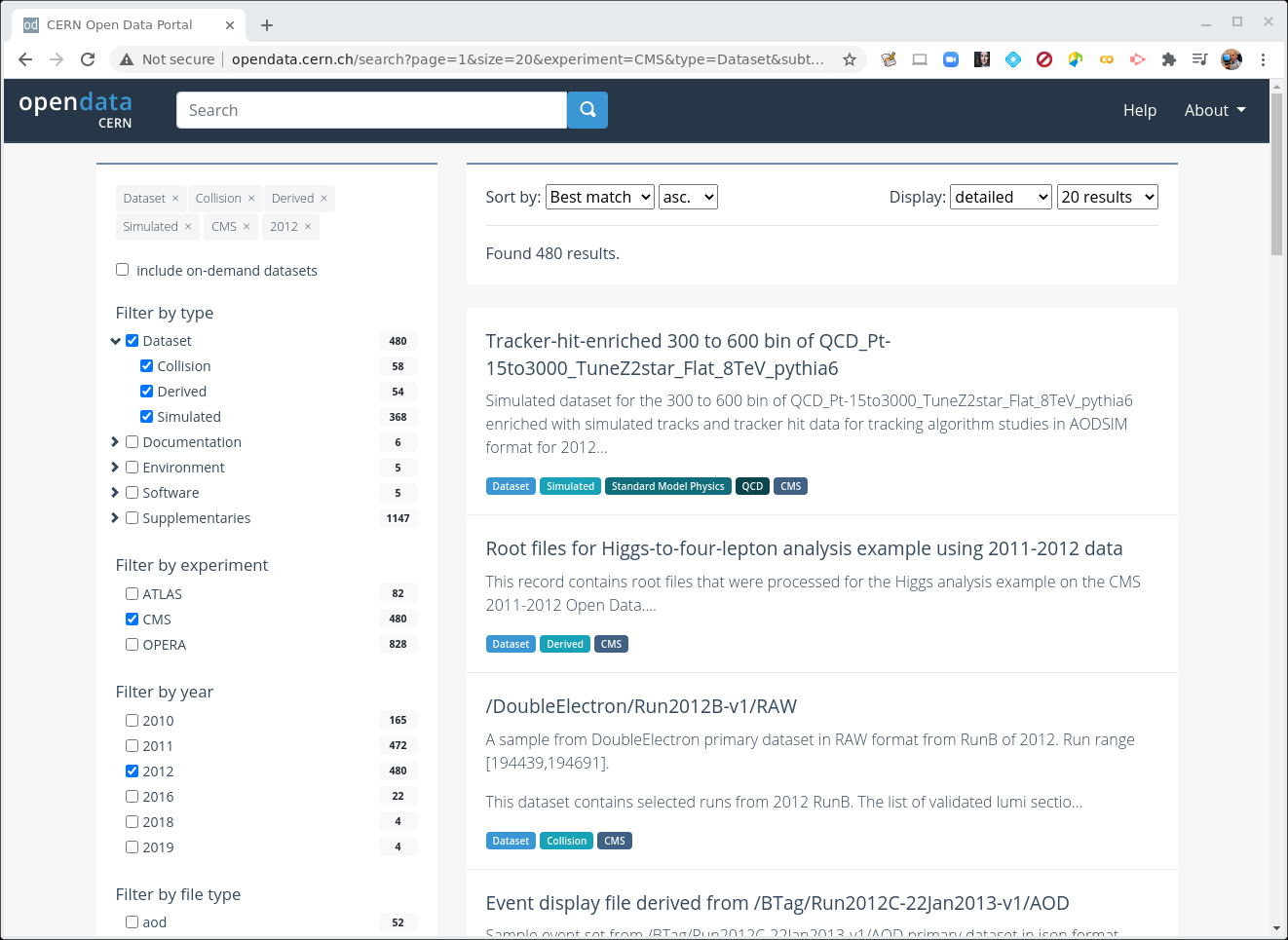
If you are coming from the previous module you should have selected CMS, Dataset, and 2012.
CERN Open Data Portal - CMS datasets
Selecting CMS, Dataset, and 2012.
Your view might look slightly different than this screenshot as the available datasets and tools are regularly updated.
When Dataset is selected, there are 3 subcategories:
- Collision refers to the real data that came off of the CMS detector.
- Derived refers to datasets that have been further processed for some specific purpose, such as outreach and education or the ispy event display.
- Simulated refers to Monte Carlo datasets.
Make a selection!
Let’s now unselect Derived and Simulation so that only the Collision option is set under Dataset.
Collision data
When you select Collision you’ll see a lot of datasets with names that may be confusing. Let’s take a look at two of them and see if we can break down these names.
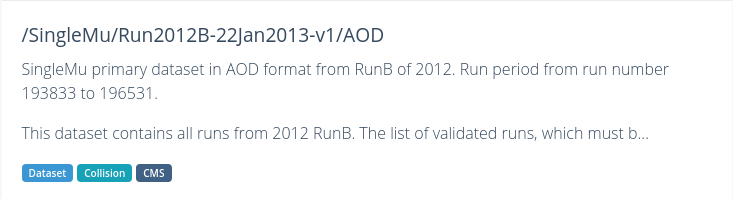
CERN Open Data Portal - CMS datasets
Some samples from the 2012 collision data
/DoubleElectron/Run2012B-v1/RAW
/SingleMu/Run2012B-22Jan2013-v1/AOD
There are three (3) parts to the names, separated by `/’.
Dataset name
DoubleElectron or SingleMu is the name of the dataset. Events stored in these primary datasets were selected by triggers of usually of a same type. For each dataset, the list of triggers is listed in the dataset record. You will learn more about them in the trigger lesson during the workshop, but for now, remind yourself that they select out some subset of the collisions based on certain criteria in the hardware or software.
Some of the dataset names are quite difficult to intuit what they mean. Others should be roughly understandable. For example,
- DoubleElectron contains mainly events with at least two electrons above a certain energy threshold.
- SingleMu contains mainly events with at least one muon above a certain momentum threshold.
- MinimumBias events are taken without any trigger or selection criteria.
Run period
Run2012B-v1 and Run2012B-22Jan2013-v1 refer to when the data were taken and in the case of the second, when the data were processed. The details are not so important for you because CMS only releases vetted data. If you were a CMS analyst working on the data as it was being processed, you might have to shift your analysis to a different dataset once all calibrations were completed.
Data format
- RAW files contain information directly from the detector in the form of hits from the TDCs/ADCs. These files are not a focus of this workshop.
- AOD stands for Analysis Object Data. This is the first stage of data where analysts can really start physics analysis.
- MINIAOD is a slimmer format of AOD, in use from Run 2 open data on. Often, the experiment will slim this down and drop some subsets of the data stream into NanoAOD, but the current open data were not yet reprocessed in that format.
Further information
If you click on the link to any of these datasets, you will find even more information, including
- The size of the dataset
- Information on the what is the recommended software release to analyze this dataset
- How were the data selected including the details of the trigger selection criteria. More on this in a later lesson.
- Validation information
- A list of all the individual ROOT files in which this dataset is stored
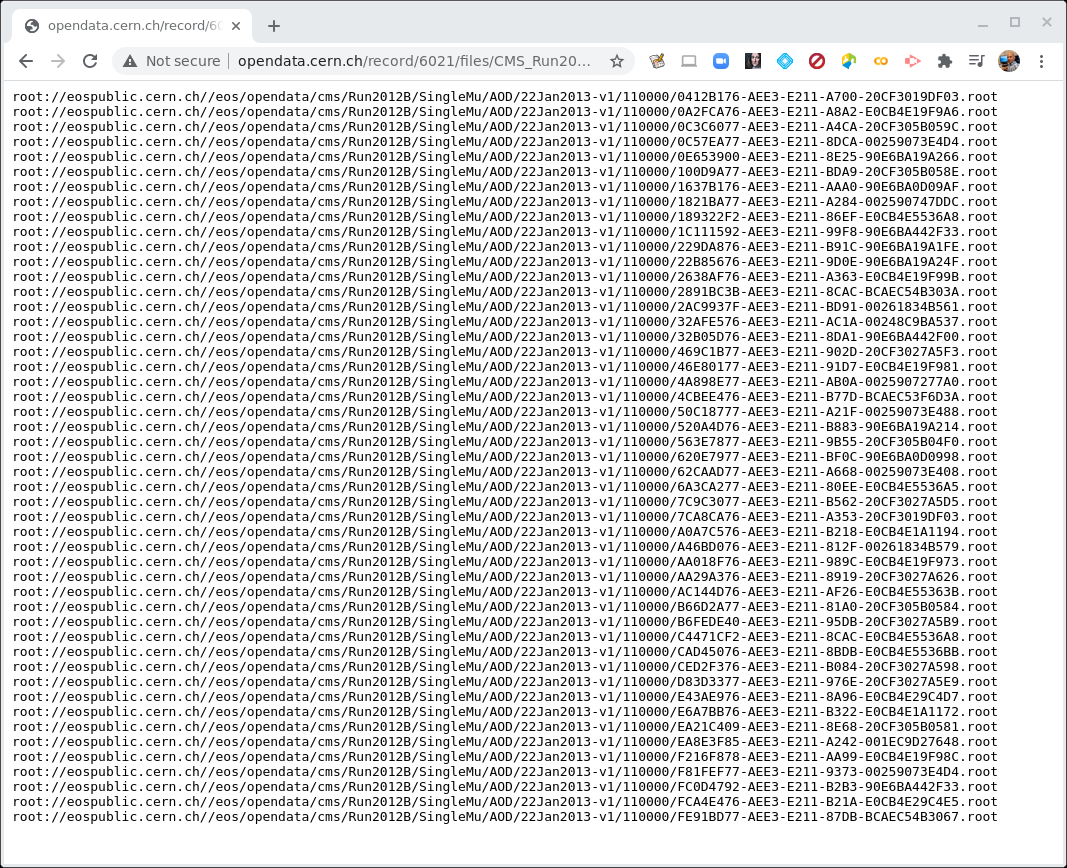
There are multiple text files that contain the paths to these ROOT files. If we click on any one of them, we see something like this.
CERN Open Data Portal - CMS datasets
Sample listing of some of the ROOT files in the /SingleMu/Run2012B-22Jan2013-v1/AOD dataset.
The prepended root: is because of how these files are accessed. We’ll use these directory
paths when we go to inspect some of these files.
Monte Carlo
We can go through a similar exercise with the Monte Carlo data. One major difference is that the Monte Carlo are not broken up by trigger. Instead, when you analyze the Monte Carlo, you will apply the trigger to the data to simulate what happens in the real data. You will learn more about this in the upcoming trigger exercise.
For now, let’s look at some of the Monte Carlo datasets that are available to you.
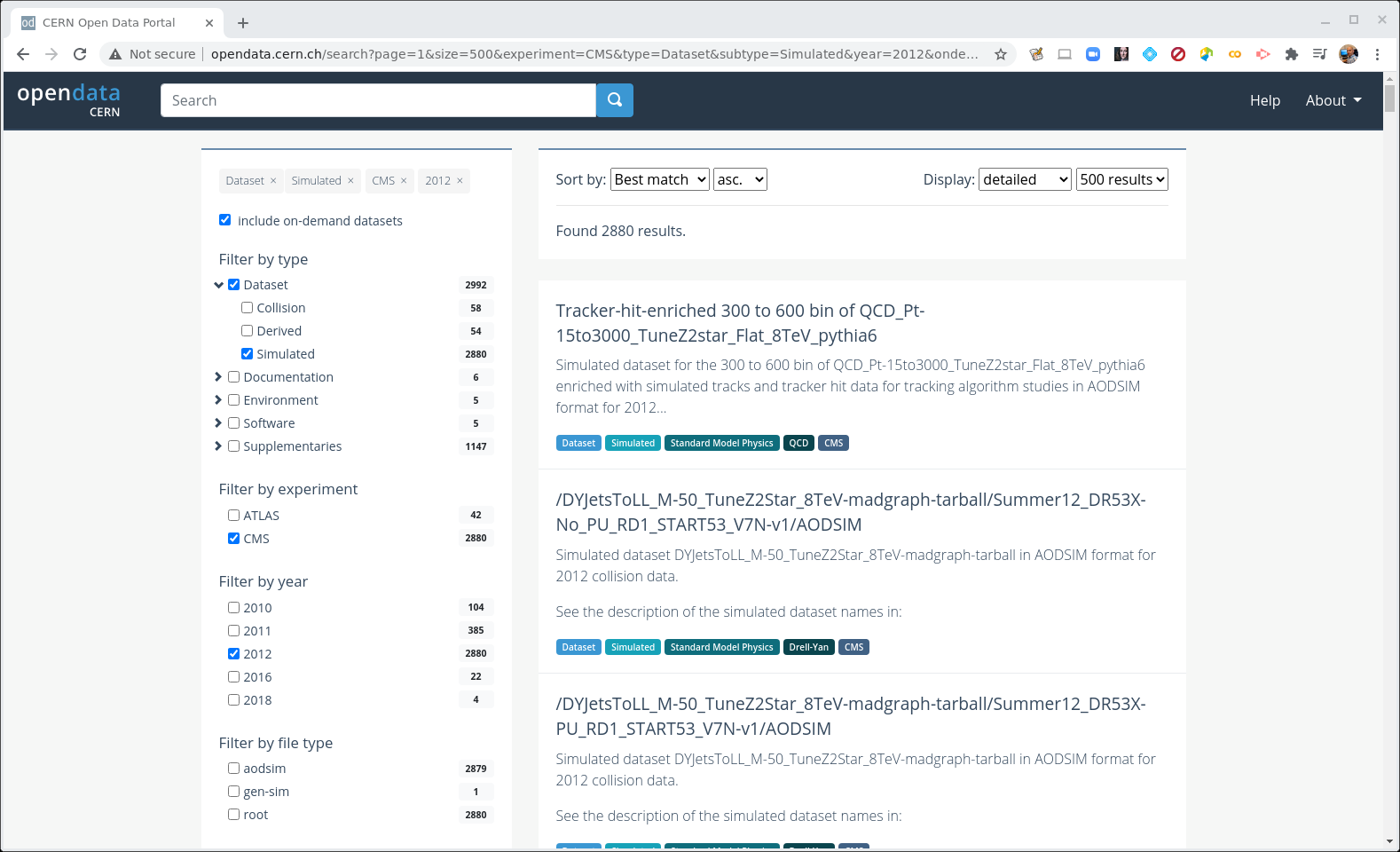
Make some selections! But first make some unselections!
Unselect everthing except for CMS, Dataset, Simulated (under Dataset) and 2012.
Next, select a new button near the top of the left-hand sidebar, include on-demand datasets. This will give us some search options related to the Monte Carlo samples.
CERN Open Data Portal - CMS datasets
Selection of the Monte Carlo dataset search options
There are a lot of Monte Carlo samples! It’s up to you to determine which ones might contribute to your background. The names try to give you some sense of the primary process, subsequent decays, the beam energy and specific simulation software (e.g. Pythia), but if you have questions, reach out to the organizers through Mattermost.
As with the collision data, here are three (3) parts to the names, separated by `/’.
Let’s look at one of them: /DYJetsToLL_M-50_TuneZ2Star_8TeV-madgraph-tarball/Summer12_DR53X-No_PU_RD1_START53_V7N-v1/AODSIM
Physics process/Monte Carlo sample
DYJetsToLL_M-50_TuneZ2Star_8TeV-madgraph-tarball is hard to understand at first glance, but if we take our time we might be able to intuit some of the meaning. This appears to simulate a Drell-Yan process in which two quarks interact to produce a virtual photon/Z boson which then couples to two leptons. The M-50 refers to a selection that has been imposed requiring the mass of the di-lepton pair to be above 50 GeV/c^2 and the remaining fields tell us something about what software was used to generate this (madgraph) the beam energy (8TeV) and some extra, quite frankly, Byzantine text. :)
Global tag
Summer12_DR53X-No_PU_RD1_START53_V7N-v1 refers to how and when this Monte Carlo was processed. The details are not so important for you because the open data coordinators have taken care to only post vetted data. But it is all part of the data provenance.
Data format
The last field refers to the data format and here again there is a slight difference.
- AODSIM or MINIAODSIM stands for Analysis Object Data - Simulation. This is the same as the AOD or MINIAOD format used in the collision data, except that there are some extra fields that store information about the original, generated 4-vectors at the parton level, as well as some other Monte Carlo-specific information.
One difference is that you will want to select the Monte Carlo events that pass certain triggers at the time of your analysis, while that selection was already done in the data by the detector hardware/software itself.
If you click on any of these fields, you can see more details about the samples, similar to the collision data.
More Monte Carlo samples
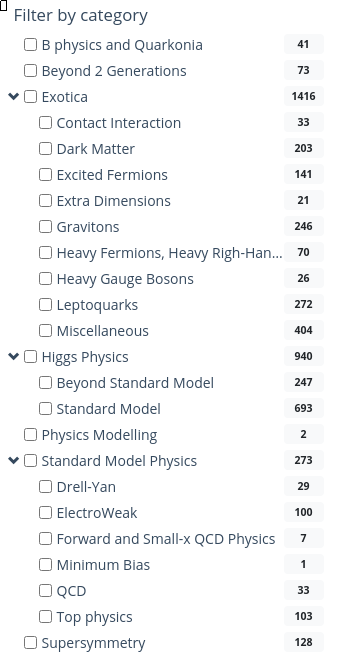
If you would like a general idea of what other physics processes have been simulated, you can check scroll down the sidebar until you come to Filter by category.
CERN Open Data Portal - CMS datasets
Selection of the Monte Carlo dataset search options
You may have to do a bit of poking around to find the dataset that is most appropriate for what you want to do, but remember, you can always reach out to the organizers through Mattermost.
Summary
By now you should have a good sense of how to find your data using the Open Data Portal’s search tools.
Key Points
The collision data are directed to different datasets based on trigger decisions
The Monte Carlo datasets contain a specific simulated physics process