Lightning overview of C++
Overview
Teaching: 5 min
Exercises: 10 minQuestions
How do I write and execute C++ code?
Objectives
To write a hello-world C++ program
Setting up your CMSSW area
If you completed the lessons on virtual machines or Docker you should already have a working CMSSW area.
-
If you are using the VM:
-
turn on your virtual machine and go to the right shell according to the validation instructions:
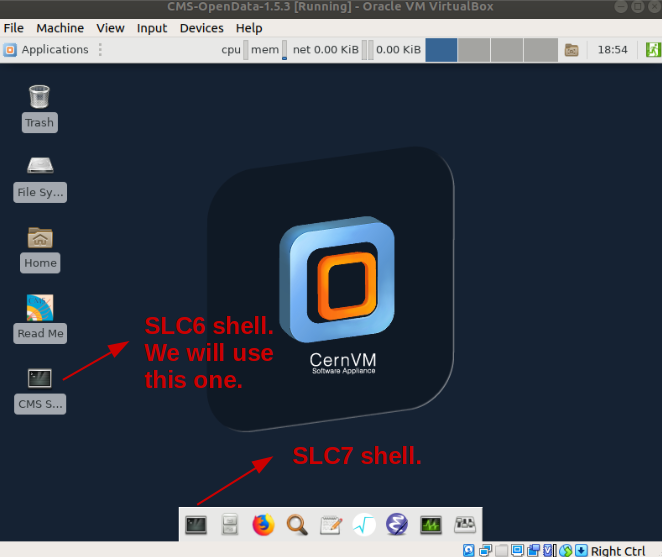
-
-
If you are using Docker:
- Start the container with:
docker start -i <theNameOfyourContainer>
- Start the container with:
Make sure you change directories to the CMSSW_5_3_32/src area; for instance, in Docker:
cd /home/cmsusr/CMSSW_5_3_32/src
Note that we are not really “installing” CMSSW but setting up an environment for it. CMSSW was already installed. This is why every time you open a new shell you will have to issue the cmsenv command, which is just a script that runs to set some environmental variables for your working area:
cmsenv
Your first C/C++ program
Let’s start with writing a simple hello world program in C. First we’ll edit the
source code with an editor of your choice.
Let’s create a new file called hello_world.cc, using your preferred editor. If
you’re using nano, you’ll type
nano hello_world.cc
or if you’re using vi, you’ll type
vi hello_world.cc
The first thing we need to do, is include some standard libraries. These libraries
allow us to access the C and C++ commands to print to the screen (stdout and stderr) as
well as other basic function.
At the very beginning of your file, add these three lines
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
The first library, cstdlib, you will see in almost every C++ program as it has many of the very
basic functions, including those to allocate and free up memory, or even just exit the program.
The second library, cstdio, contains the basic C functions to print to screen, like printf.
The third library, iostream, contains C++ functions to print to screen or write to files.
Usually people will use one or the other of the C or C++ printing functions, but for pedagogical purposes, we show you both.
Every C++ program must have a main function. So let’s define it here. The scope of this function
is defined by curly brackets { }. So let’s add
int main() {
return 0;
}
The int at the beginning tells us that this function will be returning an integer value. At the end of
the main function we have return 0, which usually means the function has run successfully to completion.
Warning!
Note that at the end of
return 0, we have a semicolon;, which is how C/C++ programs terminate lines. If you’re used to programming in python or any other language that does not use a similar terminator, this can be tough to remember. If you get errors when you compile, check the error statements for the lack of;in any of your lines!
For this function, we are not passing in any arguments so we just have the empty ( ) after the main.
This function would compile, but it doesn’t do anything. Let’s print some text to screen. Before
the return 0; line, let’s add these three lines.
printf("Hello world! This uses the ANSI C 'printf' statement\n");
std::cout << "Hello world! This uses the C++ 'iostream' library to direct output to standard out." << std::endl;
std::cerr << "Hello world! This uses the C++ 'iostream' library to direct output to standard error." << std::endl;
The text itself, should explain what they are doing. If you want to learn more about standard error and standard output, you can read more on Wikipedia.
OK! Your full hello_world.cc should look like this.
Full source code file for
hello_world.cc#include<cstdlib> #include<cstdio> #include<iostream> int main() { printf("Hello world! This uses the ANSI C 'printf' statement\n"); std::cout << "Hello world! This uses the C++ 'iostream' library to direct output to standard out." << std::endl; std::cerr << "Hello world! This uses the C++ 'iostream' library to direct output to standard error." << std::endl; return 0; }
This won’t do anything yet though! We need to compile the code, which means turning this into
machine code. To do this, we’ll use the GNU C++ compiler, g++.
Once you have saved your file and exited out of your editor, you can type this in your shell (make sure you’re in
the same directory as your hello_world.cc source code file!).
g++ hello_world.cc -o hello_world
This compiles your code to an executable called hello_world. You can now run this by typing the following on
the shell command line, after which you’ll see the subsequent output.
./hello_world
Hello world! This uses the ANSI C 'printf' statement
Hello world! This uses the C++ 'iostream' library to direct output to standard out.
Hello world! This uses the C++ 'iostream' library to direct output to standard error.
When you are working with the Open Data, you will be looping over events and may find yourself making selections based on certain physics criteria. To that end, you may want to familiarize yourself with the C++ syntax for loops and conditionals.
Key Points
We must compile our C++ code before we can execute it.